
Top stories



ESG & SustainabilityRedisa calls on govt to fix South Africa’s “broken” waste management system
2 hours


HR & Management#TopEmployers2026: Nolo Thobejane on why people power KFC’s purpose
Shan Radcliffe 4 hours

More news










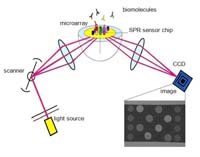
This profile can give valuable information about the progress of the disease. A unique feature of this so-called Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) technique is that it directly tests on blood serum, without complex pre-processing. A special chip will enable many parallel tests. Scientists from the University of Twente and the Radboud University Nijmegen, both in The Netherlands, will publish about the new imaging technique in the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS).
The scientists have run tests on the serum of 50 RA patients as well as a control group of 29 persons. Direct testing on blood serum is unique: in other techniques fluorescent labels and pre-processing is necessary to visualize the relevant proteins. The diluted serum is led over a special gold coated microchip containing a large number of spots with a specific peptide coating. Whenever these peptides interact with auto-antibodies present in the serum, this process can be monitored by Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging (SPR). Using laser light, all gold spots are scanned: the reflection of light of the spots changes whenever there is a molecular interaction on the spot. At a certain angle of light, there is no reflection at all: this is the so-called SPR dip undergoing a shift caused by the interaction. The technique goes beyond proving that auto-antibodies are present: the interaction between the protein and the antibody can be monitored real-time and without any labels.
Auto antibodies are manufactured by the immune system as a reaction on the so-called citrullinated proteins playing a role in rheumatoid arthritis. On a single chip, several types of peptides can be placed, for rapid parallel screening. The next step is to investigate in what way the patient profiles help to monitor the progress of the disease. This could lead to more personalized treatment in the future. The applications are not limited to monitoring rheuma or other autoimmune diseases: SPR imaging can be used for monitoring a wide range of biomolecular interactions.
The research was led by Dr. Richard Schasfoort of the BIOS Lab-on-a-chip group, part of the MESA+ Institute for Nanotechnology of the University of Twente. He has closely cooperated with the Biomolecular Chemistry group of the Radboud University Nijmegen, of Professor Ger Pruijn. It has been financed by the Dutch Technology Foundation (STW) within a project called Proteomics on a chip for monitoring autoimmune diseases.